Overview
In line with National Strategy for Transformation (NST1) 2017-2024, the industrial policy prioritizes inclusive economic growth, job creation, and private sector-led development with a focus on high-value intensive agriculture and agro-processing, manufacturing, tourism, and knowledge-based services and ICT.
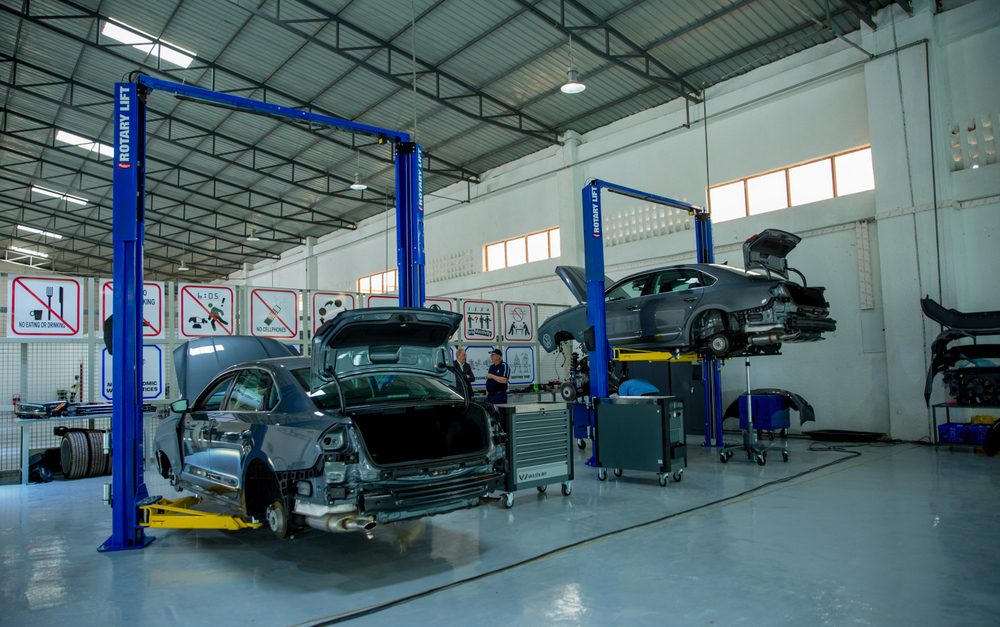
The manufacturing sector grew by 8% for the fiscal year 2017/18 from 6% in the previous financial year (Source: NISR Annual Economic Report, January 2019). The sector is still small, but it has been growing steadily. Since the adoption of the National Industrial Policy in 2011; several critical policy interventions and strategies have been developed such as Made in Rwanda policy, Entrepreneurship Development Policy (EDP), SEZ policy, the Domestic Market Recapturing Strategy (DMRS), the National Export Strategy, SMEs strategy, the National Export Strategy and Cross Border trade strategy.
To increase the local domestic and foreign supply of manufactured goods, the Government has put in place the Special Economic Zone and 9 Industrial parks in Bugesera, Rwamagana, Muhanga, Nyagatare, Musanze, Huye, Nyabihu, Rusizi, and Kicukiro. This is aimed at addressing shortcomings in the business environment by developing infrastructure, streamlining business regulations, and facilitating fast-moving investors.
For market access, Rwanda has access to African and global markets through robust free trade agreements, namely:
- Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA) with a market of 492M
- East African Community (EAC)with a market of over185M
- Tripartite Free Trade Area Agreement (COMESA EAC SADC) with a market of 600M
- Continental Free Trade Agreement (CFTA)
- Cotonou Agreement established with the EU through Everything but Arms (EBA) and conclusion of EPA
- World Trade Organization (WTO) Declarations
Rwanda has preferential access to several international markets through the WTO’s special and differential treatment provisions. This has included access to the US markets through a unilateral commitment by the US to reduce tariffs under the African Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA).
Rwanda also has access to preferential bilateral trade offers with other countries such as
China, India, Korea, Japan, and Switzerland.
INCENTIVES TO SUPPORT THE MANUFACTURING SECTOR
- Corporate income tax holiday of up to 7 years is provided when investing at least an amount equivalent to 50 million USD
- Companies with Export Processing Zones (EPZ) status are exempted from customs taxes, CIT and VAT for an investor exporting more than 80% of production
- Preferential corporate income tax rate of 15% is accorded to an investor who exports at least 50% of the production
- Registered investor shall not pay capital gains tax
- Accelerated depreciation rate of 50% for the first year
- Foreign companies investing at least 250,000 USD are allowed to recruit three foreigners without a labor test.
- Exemption of imports duties on manufacturing inputs and equipment
Please refer to the following link for more information on incentives:https://rdb.rw/wp-content/uploads/publications/Investment%20Promotion%20Law%202015%20(Investment%20code)).pdf
Public procurement policy related to manufacturing
- Government of Rwanda procurement covers ~12% of GDP
- “Made in Rwanda” policy allows for a benefit in public procurements when local value addition >30%
- Bids meeting this criterion get a 15% local preference over other bids
For any further details/information, you may require, please contact:ipd@rdb.rw
For any further details/information you may require, please contact:
NIKUZE Alice
Email: alice.nikuze@rdb.rw
Telephone: +250 788896510
Copy to:
Philip Lucky
Head of Investment Promotion & Facilitation
Email: philip.lucky@rdb.rw